 The car collision process takes only one tenth, and sometimes hundredths of a second. The basic factors influencing the size of the damage (deformation) and time, in which it takes place are the structure of the car and the speed of movement. The collision of the car with other means of transport or obstacles is accompanied by a co-operation known as an impact.
The car collision process takes only one tenth, and sometimes hundredths of a second. The basic factors influencing the size of the damage (deformation) and time, in which it takes place are the structure of the car and the speed of movement. The collision of the car with other means of transport or obstacles is accompanied by a co-operation known as an impact.
The impact is a mechanical phenomenon, taking place in the mechanical system, which is characterized by a rapid change in the velocity of points in the system in a very short period of time and conditioned by the instantaneous action of very large forces. The collision of the car with an obstacle consists of two phases:
- the first phase - the actual collision, occurring from the moment of contact to the moment of closest approach;
- the second phase - the next displacement, from the moment of the closest approach to the moment the car is disconnected.
In the first phase, the kinetic energy of relative motion is converted into permanent deformation and partially into potential elastic deformation energy., thermal energy, energy of sound vibrations and others.
In the second phase - during disconnection, the potential elastic deformation energy is converted back into the kinetic energy of the car.
The inelastic collision process ends in the first phase, a colliding, myself, the cars continue to move as one unit at the same speed.
Determining the parameters characterizing the process of a car collision requires tests. In order to confirm the reliability of the parameters obtained during the tests, this section presents an attempt to theoretically justify and examine the behavior of the car in the collision process.. The complexity of theoretical research consists in the necessity to take into account all the factors influencing the course of the collision process and the relationships between them.
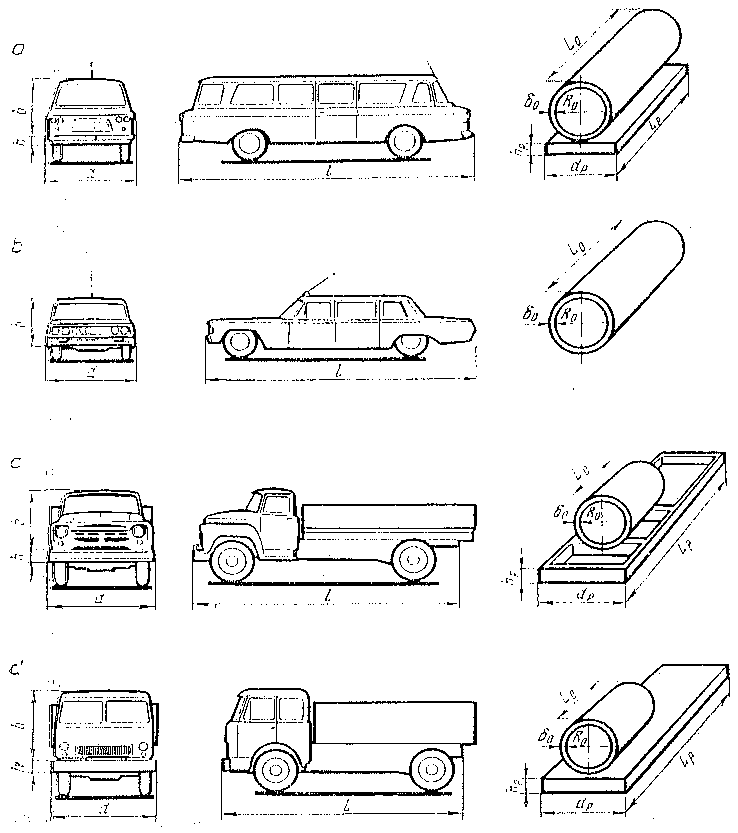
The structure of the car can be represented by the following mechanical models:
- thin-walled cylindrical shell; its mathematical model can describe passenger cars, buses and vans;
- a thin-walled cylindrical shell mounted on the cavity, shown as a flat rectangular plate or two parallel bars connected transversely; its mathematical model can describe cars having a load-bearing frame, that is, all trucks.
The purpose of the research comes down to: propose a method, theoretical justification and analysis of the method of determining all parameters accompanying a collision of cars of any brands, taking into account the presence of a human being, and on the basis of these data, finding a generalized criterion for assessing the passive safety of a car.