Battery voltage and capacity.
The nominal voltage of the battery cell - the conventional value of the voltage between the pole terminals of the cell. This value was taken equal to 2 V, although it is known, that a fully charged and fully operational cell has a slightly higher voltage, unloaded - lower.
Battery rated voltage - the conventional value of the voltage between the terminals of the battery. It is the product of the nominal cell voltage and the number of cells connected in series. Car batteries are built for voltage 6 V i 12 V (appropriately 3 and 6 cells). Maximum operating voltage (discharge) - the value of the voltage between the terminals of a fully operational battery immediately after charging. it is 2,2 V/cell, i.e.. 6,6 V for 6 volt batteries and 13,2 V for batteries with a nominal voltage of 12V.
Minimum operating voltage (discharge) - the voltage between the terminals of the battery, to which the battery can be discharged under normal operating conditions without fear of damaging it. it is 1,75 V/cell, i.e.. 5,25 V for batteries with rated voltage 6 V i 10,5 V for 12 volts. A discharge below these voltages usually leads to irreversible changes in the structure of the active masses of the plates, and thus to their accelerated wear.
Battery open circuit voltage - the value of the voltage measured between the battery terminals over time, when it is not being unloaded and loaded (open work circuit). Knowing this value, one can only infer internal damage to the battery. It cannot be related to the density of the electrolyte in the cell cells, and only to the electrolyte density in the pores of the active mass of the plates, which is impossible to measure directly. charging voltage - value of the voltage applied to the battery from the rectifier during charging. This value is determined depending on the adopted charging method (at constant current or voltage).
Gassing voltage - the value of the voltage between the terminals of the battery in the final phase of charging, when the intensive evolution of oxygen and hydrogen begins (gassing) from cells. It ranges from 2,4 into 2,45 V/cell, i.e.. from 7,2 into 7,35 V for 6-volt batteries and, accordingly, from 14.4 into 14.7 V for 12 volts.
Battery rated capacity (Qzn) — the amount of electric charge expressed in A h (ampere hours), which a fully operational and charged battery can give until reaching a normal state of discharge, i.e.. 1,75 V/cell over time 20 hours at +25°C. Capacity rated Qzn due to the discharge time condition included in its definition (20 hours) is called interchangeably twenty-hour capacity (Q20). This term together with the designation ,,Q20is more commonly used than "rated capacity", because its use does not lead to misunderstandings, which may result from identifying the rated capacity with the former equivalent of ten-hour capacity (Q10). The rated electric capacity of the battery depends on the number of plates in the cell sets and their area.
The capacitance varies depending on the discharge current, electrolyte temperature and density.
Battery rated current (lzn) - current value, that can be taken from a fully operational and charged battery over time 20 hours, until the battery reaches a state of normal discharge (1,75 V/cell). The definition of the rated current is related to the definition of the rated capacity. Typically, the term "twenty-hour current" is used instead of "rated current."20”. The rated current is calculated as follows:
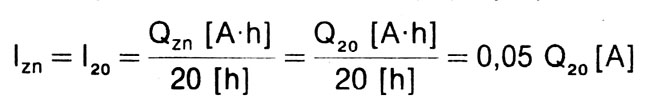
Np.: for a battery with a nominal capacity of Q20 = 34 A h, current l20 = 1,7 A, and for a battery with a capacity of Q20 = 45 A h, current l20 = 2,25 A.
Battery charging current (lorder) - the value of the current flowing through the battery during charging. Depending on the charging method and stage, different currents are used. They are defined as part of the twenty-hour capacity (Q20). Np.: Andorder = 0,05 Q20 [A]; 0,1 Q20 [A]; 0,8 Q20 [A], Thus, the numerical value of the current using the same charging method (e.g. Andorder — 0,1 Q20) for batteries of unequal electric capacity is different.
Electrolyte density - indicates the state of charge of the battery under condition, that the measurement is made at least after 30 minutes from the time of its completion or charging, or after 24 h since the electrolyte was replenished and that the change in electrolyte density was the result of normal electrochemical changes in the battery. Because the density of the electrolyte changes with temperature, adopted for unambiguous determination of battery states, characteristic densities are given at the so-called. reference temperature, i.e.. + 25°C. It means, that if the density was measured, for example,. at 0°C, to determine the actual battery charge level, the measured density value should be converted to the reference temperature. The unit of density is [g/cm3]. It is also defined according to the Baume scale [°Be], however, it is not used in practice in the country.
Characteristic densities:
1,28 g/cm3 — battery fully charged,
1,14 g/cm3 — limit of allowable electrolyte density at normal discharge of the battery,
1,1 g/cm3 — the battery is fully discharged.